I wrote about Postmodern ERP for Bluevision Mail this month, but I would like to discuss more details on postmodern ERP development and global strategy for the global companies in more detail.
Contents
What is postmodern ERP
Postmodern ERP is a technology strategy that automates and links administrative and operational business capabilities
(such as finance, HR, purchasing, manufacturing and distribution) with appropriate levels of integration that balance the benefits of vendor-delivered integration against business flexibility and agility. This definition highlights that there are two categories of ERP strategy: administrative and operational.
With Core ERP as the center, we refer to the whole global group ERP system that combines cloud ERP, SaaS Application etc. around.
In the latter half of 1990 and 2000, each company replaced and implemented the disparate business applications to an integrated business application ERP and deployed it through related subsidiaries. However, the global business environment is changing drastically, it will become difficult to operate with only the conventional core ERP, at the same time the global companies needs to use flexible and innovative cloud-based application for differentiation and expansion of business from other companies.
Currently it is becoming a flow of hybrid ERP composed of Core ERP and cloud-based ERP applications.
Hybrid ERP model and Pace-Layered Strategy
As for hybrid type ERP, there is Core ERP such as accounting, sales and purchasing of core business mainly as follows, so as to supplement around it, we will work together with Cloud ERP to build business of the entire company It is Hybrid ERP model as postmodern ERP.
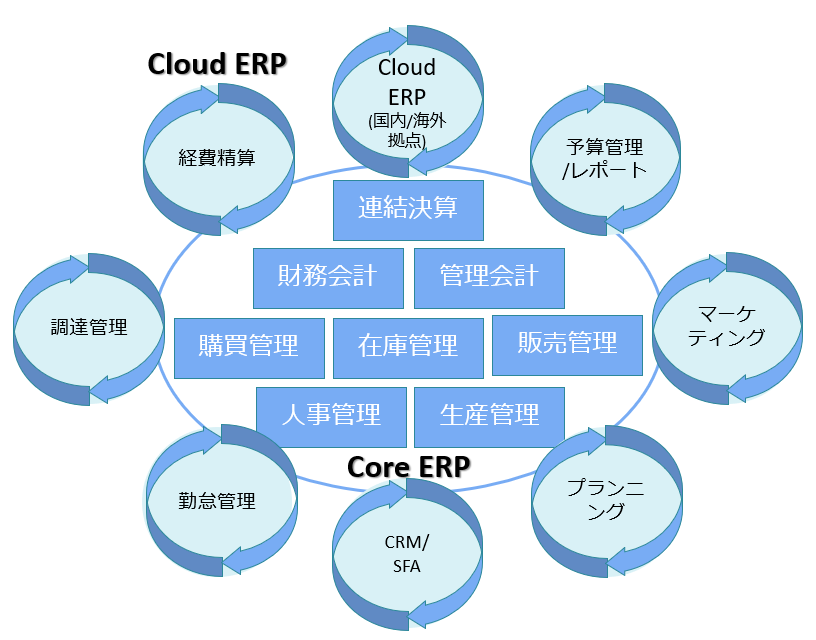
Cloud ERP can also be used in one business division, not the whole company, and flexibility to expand to the entire company can be accommodated depending on the situation.
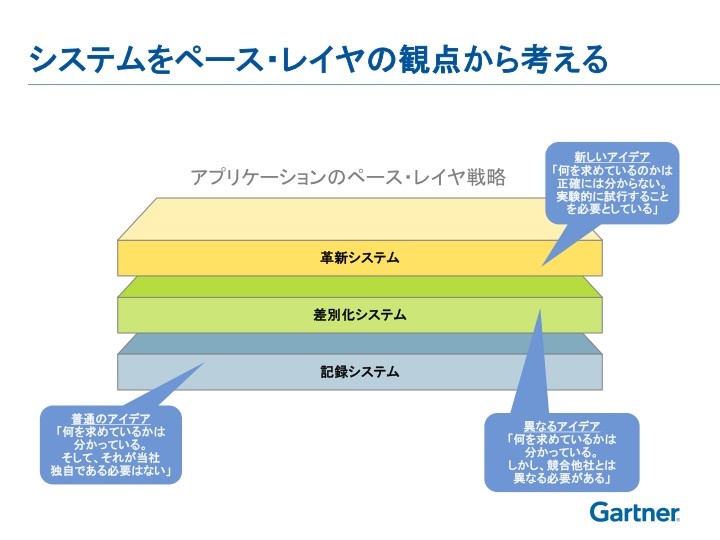
Pace-Layered strategy advocated by Gartner is a reference that serves as a core business application strategy. Pace-Layered strategy is a concept of “classifying functions that Core ERP has in its pace layer of “recording”, “differentiation”, and “innovation”, and in addition to this, how to expand to group companies will become important in the future I will come.
ERP Global deployment strategy
Some Japanese companies have already deployed Core ERP and are deploying them to domestic subsidiaries in Japan and overseas subsidiaries, but from the perspective of global deployment they are still working to move forward with strategies and plans for ERP applications including overseas.
Each company has its own judgment as to which product such as SAP and Oracle and range of Core ERP of business application, but including Cloude ERP to supplement it, it is necessary that expand to deploy it including overseas subsidiaries more quickly, cheaply and flexibly in near future.
So, what is important from my experience until now is to classify the importance of the company / business division and the regional importance of the subsidiary within the group companies and proceed to global deployment.
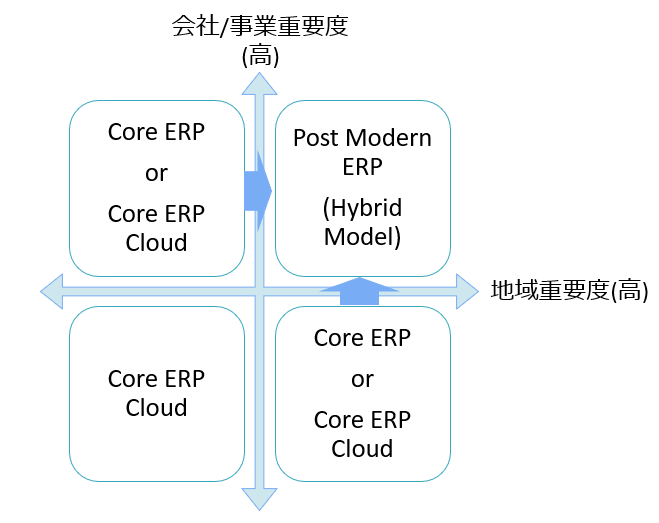
For example, in the case of an important base in the US headquarters for Japanese company, it will be deployed in the Core ERP template and Cloud ERP model as same as in the Japanese headquarters, but in the case where it will be the small subsidiary in the United States as well, it is possible to develop Core ERP templates , or while deploying cloud-based Core ERP Cloud, as the importance increases, it will expand to a hybrid model more.
The speed of deploying becomes very important as the point of global deployment. Currently the project plan and approach to implement to only 1 company over many years may be risk of existing systems becoming obsolete at the completion of global implementation project and having a gap between the new business model and the existing system.
From now on, it is necessary to standardize company systems and operations globally, and to have core businesses and systems that can respond flexibly to new business. We will deploy it while classifying the importance and priority of subsidiary companies and group companies, so we can deploy it globally more quickly and streamline the business management, data visualization and data utilization throughout the group ERP systems.
Postmodern ERP business case in Japan
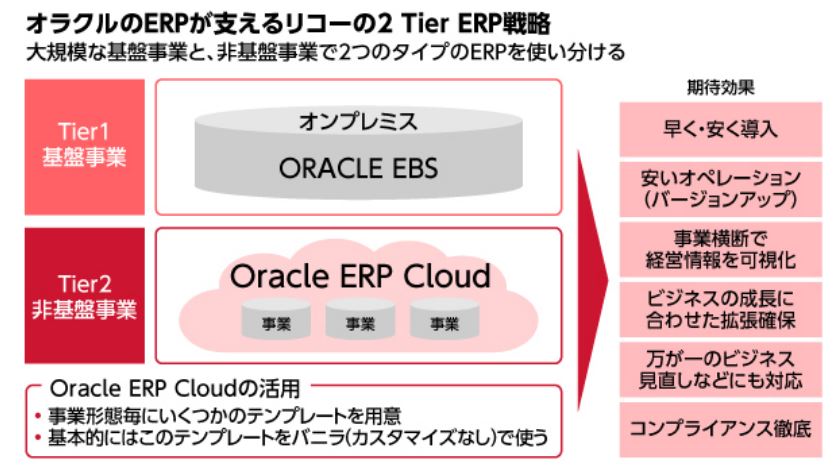
Here, as a global deployment example of one postmodern ERP, Ricoh’s Oracle EBS deployment strategy may be helpful for Japanese companies that have already used Core ERP at Japanese headquarters.
http://diamond.jp/articles/-/142644
They are taking the “2 Tier ERP Strategy” that selectively uses ERP systems for core business of their multifunction machine business which is the current business and small business such as new business.
The point here is the following comment.
- “I tried to use ERP Cloud, which enables the speedy launch and expansion of business in peripheral business and new business areas that are Tier 2” (Mr. Ishino Ricoh Executive Officer)
- Public cloud can be introduced speedily, and the cost of operation maintenance can be reduced.
- In the cloud project, Top-down approach is indispensable that “adapts the business to the system”. The most important thing to make that approach successful is to firmly engage and get their commitment with the business owner such as the business department manager
- “If you think that the functions of ERP Cloud are different or not much your business requirements, it is their way of doing wrong.”
Postmodern ERP global maintenance strategy
For postmodern ERP, it is the global maintenance strategy as important as the deployment strategy. How to support and maintain after global deployment to develop the benefits of ERP, how to manage, extend, user training and security of company-wide management data we have to consider the global maintenance strategy not only from the system operation cost but also from a global perspective.
One method of maintenance strategy is to divide the global whole for each regions and to manage the system maintenance. For example, it is to classify it as Japan region, Asia region, America (North and South America) region, EMEA (Europe Africa) region 4 regions, or 3 regions combined Japan and Asia combined as one Asian region.
The reason for separating these regions is that you can cover the same time difference first, and the other different regions can support your regions at night. In addition, the common languages supported by each regions are similar. If it is an Americas region, it is English or Spanish, if it is an Asian region, Chinese, or English.
Regarding operation and maintenance of the whole postmodern ERP system, strategies and maintenance organization are needed from a global perspective such as cost, support, security, etc., by taking advantage of offshore.
Next step of postmodern ERP
Regarding the next step of postmodern ERP, I told you that we are transitioning to a hybrid model combining on-premises and clouds ERP, but as a next step, I think that we will shift to an all-in-one cloud-based ERP model from on-premises.
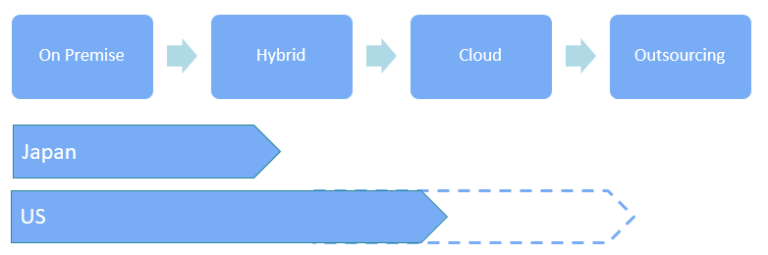
Realistically, even in the case of American companies, there are also examples of clients that completely revamp the cloud ERP directly from the on-premises ERP to the cloud ERP rather than the hybrid model, which is a combination with the cloud ERP. In order to shift to cloud ERP in the future, expansion of functional scope and ease of integration with other systems will be key points, and some companies will gradually shift to cloud-based ERP around 2020.
Next to the cloud ERP, there may be companies that focus only on the core competence of their business and transit to outsource all the way to back office operations, manage business management data, analysis and global system maintenance.